The 7 Dimensions of ABA
Since many years ago, ABA specialists have used the 7 ABA dimensions to deliver clients with precise and successful research-based solutions. In order to guarantee that each client’s needs are satisfied in a methodical and data-driven manner, they are utilized in the treatment planning for those getting ABA therapy, primarily those with autism or other developmental disorders.
ABA has many facets. These dimensions are known as effectiveness, relevance, systematicity, and social significance. Let’s examine each one in turn. How effective is ABA, how relevant is it, and how does it compare with other approaches? This article aims to provide an overview of the seven dimensions of ABA. You can also find examples of ABA in action through video examples. Whether or not ABA is right for your child will depend on their particular needs. An individual’s treatment plan must have goals following these seven dimensions:
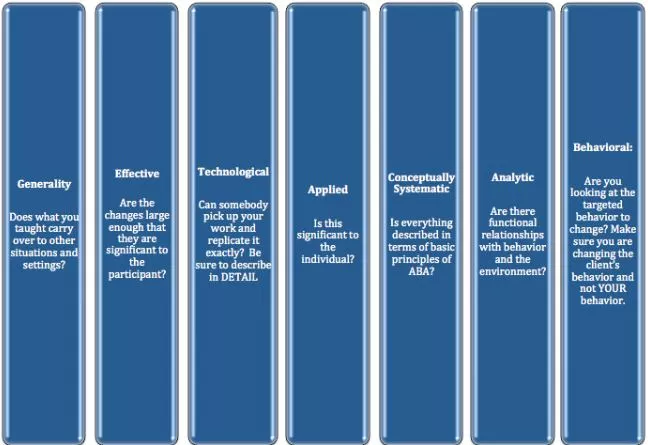
1) Generality
2) Effective
3) Technological
4) Applied
5) Conceptually Systematic
6) Analytic
7) Behavioral.
7 Dimensions of ABA Explanation
General
If the behavior is intended to be changed, the change shouldn’t be programmed to happen at the time or for a brief duration. The change in behavior, which is the abilities gained through treatment, should stand up to the tests of time. Additionally, it should be sustained across various environments and people even after the treatment.
Most of the time, ABA occurs in a controlled, sterile, or more clinical context. While programming may initially occur in these settings, the treatment must be planned to reflect the person’s environment. In this way, we can ensure that the same behavior can be observed in different situations outside of treatment and will be maintained throughout treatment. It is best to ensure that your staff is consistent throughout your child’s treatment. However, the child must be able to practice their techniques with other children and staff. The treatment will not be practical or efficient until it is generalized.
Effective
The goals should reflect and reflect the individual client as well as the culture of their local community. However, equally important, the methods used to achieve them should be efficient. It is important to inquire: “Is the intervention working? “Am I seeing the data going in the desired direction?” These are questions that can be answered with regular monitoring of the progress of data collection and observing the actions being used.
Technological
A written intervention must be composed in a manner that contains all the necessary components clearly and precisely so that anyone can replicate the procedure. The strategies that make up an intervention must be identified and explained to ensure this. For instance, think about your most-loved Pinterest recipe to bake a cake. It’s well-written, easy to comprehend, and execute. Even my husband can master it!. Implementing behavioral interventions on individuals is more complex; however, it is expected to be based on the same principles. Let’s assume that the procedure is confusing or written in a way that is unclear and the likelihood that all on the treatment team are similarly applying treatment is not high. When treatment is technologically based, it is simple to replicate, and treatment quality is exceptionally high.
Apply
The term”applicable” is used to describe the implementation of ABA interventions within society after conducting research in a lab. Behavior Analysts must concentrate on the implementation aspects of ABA to alter socially significant behavior. The specific treatment goals that are decided on as the primary concentration is determined by their importance to the individual and the family members of the individual. The socially significant behavior of each person is unique to them, and they are the abilities that allow them to operate in their surroundings better and effectively. To be considered legitimate in a social context, it has to bring about a significant change that lasts for a long time.
What would be a suitable way to address the issue if children are engaging in tantrums because they cannot communicate their needs and desires effectively? Learning to teach the child how efficiently communicate needs and desires is an acceptable social objective. It could immediately impact the child’s daily life and the lives of people who interact with him regularly (family members or teachers, classmates). When considering treatment interventions that aim at improving behavior, the team should consider how important the targeted behavior change will be for the child.
A conceptually systematic
If any intervention can be conceptually logical, it implies that its research is grounded and reflects the fundamental principles of applied behavioral analysis. A crucial question to consider is: “Is this intervention consistent with principles that have been determined to be effective as defined in the research?”
Analytic
Analytical means looking over the data to make data-driven decisions. This means that the data collected must be gathered on interventions. In looking at information, if an intervention isn’t producing a change or increase in the desired behavior, then the intervention should be modified. When the intervention has been modified, and the data show an increase in the desired direction, it is possible to establish an established relationship between the intervention and the rise of positively oriented behavior. This is a way to address the issue of credibility: can the intervention in use and the data demonstrating the changes sufficient to establish a solid functional connection?
Behavioral
The behavior must be observed and quantifiable to change it. If we can observe behavior, see it, and measure it using information, we can alter it (Gilmore 2019). The term “behavior” doesn’t necessarily mean “bad” behavior, but it can also refer to acceptable or desirable. Behavior Analysts aim to improve specific behaviors and reduce other ones. It is also crucial to define “behavior change” in terms of how a child’s life is altered, not only their behavior.
Understanding the seven aspects of Applied Behavior Analysis and how it is integrated into your daughter or son’s objectives and program will allow you to make more significant changes that will have a more considerable impact.
Most Important dimensions from the 7 Dimensions of ADA
Effectiveness
Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is based on scientific methods and principles. It uses seven core dimensions to guide its treatment programs. Each intervention must be socially significant, research-based, and practical. In addition, each intervention must be monitored and evaluated to ensure it achieves its goals. Evidence-based outcomes also support ABA. In addition, the seven dimensions of ABA are central to the success of any treatment program.
ABA therapies are built on the seven core dimensions outlined by Baer, Wolf, and Risley. Each intervention falls under one of these dimensions. ABA therapists use an acronym known as GET A CAB to help parents remember the components of their therapy. Effective interventions must have a positive impact on a child’s behavior. Therefore, all seven dimensions of ABA should be considered when formulating a child’s treatment plan.
Applied behavior analysis programs focus on the social behaviors of their clients. BCBAs use a variety of behavior change agents, including the child’s RBT, parents, and other specialists. Behavioral change agents work together to ensure clients achieve socially essential goals in any environment. The interventions address each client’s specific needs while keeping the goals in mind.
Behavioral interventions are considered adequate when they produce measurable, practical effects. This means that they must be technologically advanced, and their effects must be large enough to be effective. ABA methods must be simple to understand, concise, and detailed. If they don’t meet these criteria, they are not effective. This definition is also not practical in clinical practice. ABA practitioners must be aware of the limitations of their behavioral interventions.
Relevance
A common concern in implementing ABA is ensuring that research findings are relevant to decision-making. While external validity pertains to the extent to which research results can be applied to various settings, relevance is the degree to which research findings are relevant to a specific situation. Evidence is more relevant if it matches the essential characteristics of a client, specific treatment, or contextual factors. These variables may include the social and physical environment, staff skills, and the organization’s capacity.
In addition to research-based methods, ABA relies on seven core dimensions that should guide all interventions that are offered through ABA services. These interventions must be socially significant, supported by research, and closely monitored. Any interventions that are not effective can be modified or stopped altogether. As a result, the results of ABA interventions are more likely to be relevant. Moreover, research-based methods are often more effective when implemented by professionals who understand behavioral science and its limitations.
ABA also focuses on direct measurements of actual behavior. Behavior is a series of events that take place in the physical environment. Observation and practical experience are the primary factors that guide ABA. Behavior intervention programs focus on teaching and observing the behaviors of the child. It is crucial to note that the effectiveness of the techniques in ABA depends on the generality of these outcomes. The goals of behavior change interventions are also relevant to the needs of each individual.
Ultimately, the best way to decide whether ABA is relevant to a given situation is to apply it to a particular population. Evidence-based ABA practitioners should ideally rely on well-controlled experiments with the same population. Otherwise, they should use the highest quality research possible. But this is often not possible. In some cases, practitioners may rely on a single study and a small sample.
Systematicity
According to the advocates of ABA, the child’s treatment should be conceptually systematic. This means that all the techniques used should be derived from the ABA principles and consistent with what has been demonstrated in the literature. It should also be measurable, as the goals of ABA therapy are to improve a child’s behavior. To achieve this, ABA practitioners use a series of methods and focus on the specific behaviors that are important to them and others.
Because of its scientific nature, applied behavior analysis is based on the principles of the seven core dimensions. All ABA interventions must fall under one of these dimensions. These interventions must be based on proven, evidence-based methods, be practical and meaningful, and be closely monitored and modified when they are not working. The research that supports the ABA principles is also critical to the success of ABA treatments.
Systematicity is one of the seven dimensions associated with ABA. Using scientific data to analyze behavior lets practitioners identify variables responsible for changing the learner’s behavior. This approach, in turn, improves the learner’s social behavior and quality of life. Since the learning process is individualized, behavior change goals are set. A customized intervention based on the individual’s needs will maximize the effects of the intervention.
Social significance
In applied behavior analysis, behaviors that have social significance are targeted. During ABA therapy, a client’s ABA services should be tailored to the behavior’s social significance and relevance to the client. Socially significant behaviors are valuable to the client’s quality of life and can have long-term effects. They are typically determined by the client’s age, reinforcement in the natural environment, and caregivers’ needs. Here are some examples of socially significant behaviors:
The social significance of behavior interventions is essential for an individual’s ability to function in their environment. The behavior may be essential for a person to cross a street safely, or it might be as simple as ordering lunch in the cafeteria. The range of behaviors that ABA targets are extensive and profound. Learning to communicate with others is an example of social significance. It is important to realize that socially significant behaviors are essential for functioning in the world around us.
In addition to the social importance of ABA, some studies have also examined the impact of ABA on consumer behavior. Ilene Schwartz, for example, wrote an article in which she suggested that ABA services are tied to consumer satisfaction and education. In other words, the social validity of an ABA service has to be a reflection of how consumers react to the service. However, while the article discussed social validity, it is essential to note that this is not a comprehensive list of factors that determine whether a product is socially valid.
The importance of ABA as science is discussed in the Gulf region and Saudi Arabia context. ABA Through the Looking Glass Symposium highlights how the field has evolved and how it impacts the lives of children and their parents. Furthermore, workshops will be held for families and professionals who are interested in learning more about the benefits of ABA. There will also be discussions about the future of the field in this region. So, it is essential to understand the social significance of ABA before implementing it.
Analytical component
The seven dimensions of ABA therapy are based on scientific methods and core principles. All interventions provided through ABA services must fall within one of these principles. Each intervention must be supported by research, practical and socially significant, and monitored closely to ensure it works. Additionally, every intervention should be adapted and evaluated if it is not practical. The seven dimensions also provide a framework for developing and evaluating behavioral interventions.
In ABA, the analytical component is considered successful when the analyst manipulates the target behavior in a controlled laboratory environment. This can be relatively easy in a controlled laboratory but impossible outside. There are two ethical methodologies for manipulating target behavior: multiple baseline design and reversal design. In addition to these, the authors outline their methodology for manipulating behavior. Finally, the authors suggest a method that combines these two aspects of ABA.
The social significance of behavior is another crucial factor in ABA. For example, nonapplied researchers might study how people eat. The latter, meanwhile, may attempt to change the eating behaviors of individuals. This difference in approach is the key to ABA’s effectiveness. The research must be able to measure and observe the behavior to make the intended changes. By understanding the seven dimensions of ABA, you will be better equipped to implement effective behavioral change.
ABA is a scientifically validated treatment for people with autism. Registered behavior technicians and Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) identify the reasons behind the behavior and use data-driven analysis to determine appropriate strategies to increase independence. The methods used to treat autism are based on decades of published research. ABA treatment plans are based on the seven dimensions. A good ABA program will have a variety of strategies to encourage independence in the child.
The 7 Dimensions of ABA
Since many years ago, ABA specialists have used the 7 ABA dimensions to deliver clients with precise and successful research-based solutions. In order to guarantee that each client’s needs are satisfied in a methodical and data-driven manner, they are utilized in the treatment planning for those getting ABA therapy, primarily those with autism or other developmental disorders.
ABA has many facets. These dimensions are known as effectiveness, relevance, systematicity, and social significance. Let’s examine each one in turn. How effective is ABA, how relevant is it, and how does it compare with other approaches? This article aims to provide an overview of the seven dimensions of ABA. You can also find examples of ABA in action through video examples. Whether or not ABA is right for your child will depend on their particular needs. An individual’s treatment plan must have goals following these seven dimensions:
1) Generality
2) Effective
3) Technological
4) Applied
5) Conceptually Systematic
6) Analytic
7) Behavioral.
7 Dimensions of ABA Explanation

General
If the behavior is intended to be changed, the change shouldn’t be programmed to happen at the time or for a brief duration. The change in behavior, which is the abilities gained through treatment, should stand up to the tests of time. Additionally, it should be sustained across various environments and people even after the treatment.
Most of the time, ABA occurs in a controlled, sterile, or more clinical context. While programming may initially occur in these settings, the treatment must be planned to reflect the person’s environment. In this way, we can ensure that the same behavior can be observed in different situations outside of treatment and will be maintained throughout treatment. It is best to ensure that your staff is consistent throughout your child’s treatment. However, the child must be able to practice their techniques with other children and staff. The treatment will not be practical or efficient until it is generalized.
Effective
The goals should reflect and reflect the individual client as well as the culture of their local community. However, equally important, the methods used to achieve them should be efficient. It is important to inquire: “Is the intervention working? “Am I seeing the data going in the desired direction?” These are questions that can be answered with regular monitoring of the progress of data collection and observing the actions being used.
Technological
A written intervention must be composed in a manner that contains all the necessary components clearly and precisely so that anyone can replicate the procedure. The strategies that make up an intervention must be identified and explained to ensure this. For instance, think about your most-loved Pinterest recipe to bake a cake. It’s well-written, easy to comprehend, and execute. Even my husband can master it!. Implementing behavioral interventions on individuals is more complex; however, it is expected to be based on the same principles. Let’s assume that the procedure is confusing or written in a way that is unclear and the likelihood that all on the treatment team are similarly applying treatment is not high. When treatment is technologically based, it is simple to replicate, and treatment quality is exceptionally high.
Apply
The term”applicable” is used to describe the implementation of ABA interventions within society after conducting research in a lab. Behavior Analysts must concentrate on the implementation aspects of ABA to alter socially significant behavior. The specific treatment goals that are decided on as the primary concentration is determined by their importance to the individual and the family members of the individual. The socially significant behavior of each person is unique to them, and they are the abilities that allow them to operate in their surroundings better and effectively. To be considered legitimate in a social context, it has to bring about a significant change that lasts for a long time.
What would be a suitable way to address the issue if children are engaging in tantrums because they cannot communicate their needs and desires effectively? Learning to teach the child how efficiently communicate needs and desires is an acceptable social objective. It could immediately impact the child’s daily life and the lives of people who interact with him regularly (family members or teachers, classmates). When considering treatment interventions that aim at improving behavior, the team should consider how important the targeted behavior change will be for the child.
A conceptually systematic
If any intervention can be conceptually logical, it implies that its research is grounded and reflects the fundamental principles of applied behavioral analysis. A crucial question to consider is: “Is this intervention consistent with principles that have been determined to be effective as defined in the research?”
Analytic
Analytical means looking over the data to make data-driven decisions. This means that the data collected must be gathered on interventions. In looking at information, if an intervention isn’t producing a change or increase in the desired behavior, then the intervention should be modified. When the intervention has been modified, and the data show an increase in the desired direction, it is possible to establish an established relationship between the intervention and the rise of positively oriented behavior. This is a way to address the issue of credibility: can the intervention in use and the data demonstrating the changes sufficient to establish a solid functional connection?
Behavioral
The behavior must be observed and quantifiable to change it. If we can observe behavior, see it, and measure it using information, we can alter it (Gilmore 2019). The term “behavior” doesn’t necessarily mean “bad” behavior, but it can also refer to acceptable or desirable. Behavior Analysts aim to improve specific behaviors and reduce other ones. It is also crucial to define “behavior change” in terms of how a child’s life is altered, not only their behavior.
Understanding the seven aspects of Applied Behavior Analysis and how it is integrated into your daughter or son’s objectives and program will allow you to make more significant changes that will have a more considerable impact.
Most Important dimensions from the 7 Dimensions of ADA
Effectiveness
Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is based on scientific methods and principles. It uses seven core dimensions to guide its treatment programs. Each intervention must be socially significant, research-based, and practical. In addition, each intervention must be monitored and evaluated to ensure it achieves its goals. Evidence-based outcomes also support ABA. In addition, the seven dimensions of ABA are central to the success of any treatment program.
ABA therapies are built on the seven core dimensions outlined by Baer, Wolf, and Risley. Each intervention falls under one of these dimensions. ABA therapists use an acronym known as GET A CAB to help parents remember the components of their therapy. Effective interventions must have a positive impact on a child’s behavior. Therefore, all seven dimensions of ABA should be considered when formulating a child’s treatment plan.
Applied behavior analysis programs focus on the social behaviors of their clients. BCBAs use a variety of behavior change agents, including the child’s RBT, parents, and other specialists. Behavioral change agents work together to ensure clients achieve socially essential goals in any environment. The interventions address each client’s specific needs while keeping the goals in mind.
Behavioral interventions are considered adequate when they produce measurable, practical effects. This means that they must be technologically advanced, and their effects must be large enough to be effective. ABA methods must be simple to understand, concise, and detailed. If they don’t meet these criteria, they are not effective. This definition is also not practical in clinical practice. ABA practitioners must be aware of the limitations of their behavioral interventions.
Relevance
A common concern in implementing ABA is ensuring that research findings are relevant to decision-making. While external validity pertains to the extent to which research results can be applied to various settings, relevance is the degree to which research findings are relevant to a specific situation. Evidence is more relevant if it matches the essential characteristics of a client, specific treatment, or contextual factors. These variables may include the social and physical environment, staff skills, and the organization’s capacity.
In addition to research-based methods, ABA relies on seven core dimensions that should guide all interventions that are offered through ABA services. These interventions must be socially significant, supported by research, and closely monitored. Any interventions that are not effective can be modified or stopped altogether. As a result, the results of ABA interventions are more likely to be relevant. Moreover, research-based methods are often more effective when implemented by professionals who understand behavioral science and its limitations.
ABA also focuses on direct measurements of actual behavior. Behavior is a series of events that take place in the physical environment. Observation and practical experience are the primary factors that guide ABA. Behavior intervention programs focus on teaching and observing the behaviors of the child. It is crucial to note that the effectiveness of the techniques in ABA depends on the generality of these outcomes. The goals of behavior change interventions are also relevant to the needs of each individual.
Ultimately, the best way to decide whether ABA is relevant to a given situation is to apply it to a particular population. Evidence-based ABA practitioners should ideally rely on well-controlled experiments with the same population. Otherwise, they should use the highest quality research possible. But this is often not possible. In some cases, practitioners may rely on a single study and a small sample.
Systematicity
According to the advocates of ABA, the child’s treatment should be conceptually systematic. This means that all the techniques used should be derived from the ABA principles and consistent with what has been demonstrated in the literature. It should also be measurable, as the goals of ABA therapy are to improve a child’s behavior. To achieve this, ABA practitioners use a series of methods and focus on the specific behaviors that are important to them and others.
Because of its scientific nature, applied behavior analysis is based on the principles of the seven core dimensions. All ABA interventions must fall under one of these dimensions. These interventions must be based on proven, evidence-based methods, be practical and meaningful, and be closely monitored and modified when they are not working. The research that supports the ABA principles is also critical to the success of ABA treatments.
Systematicity is one of the seven dimensions associated with ABA. Using scientific data to analyze behavior lets practitioners identify variables responsible for changing the learner’s behavior. This approach, in turn, improves the learner’s social behavior and quality of life. Since the learning process is individualized, behavior change goals are set. A customized intervention based on the individual’s needs will maximize the effects of the intervention.
Social significance
In applied behavior analysis, behaviors that have social significance are targeted. During ABA therapy, a client’s ABA services should be tailored to the behavior’s social significance and relevance to the client. Socially significant behaviors are valuable to the client’s quality of life and can have long-term effects. They are typically determined by the client’s age, reinforcement in the natural environment, and caregivers’ needs. Here are some examples of socially significant behaviors:
The social significance of behavior interventions is essential for an individual’s ability to function in their environment. The behavior may be essential for a person to cross a street safely, or it might be as simple as ordering lunch in the cafeteria. The range of behaviors that ABA targets are extensive and profound. Learning to communicate with others is an example of social significance. It is important to realize that socially significant behaviors are essential for functioning in the world around us.
In addition to the social importance of ABA, some studies have also examined the impact of ABA on consumer behavior. Ilene Schwartz, for example, wrote an article in which she suggested that ABA services are tied to consumer satisfaction and education. In other words, the social validity of an ABA service has to be a reflection of how consumers react to the service. However, while the article discussed social validity, it is essential to note that this is not a comprehensive list of factors that determine whether a product is socially valid.
The importance of ABA as science is discussed in the Gulf region and Saudi Arabia context. ABA Through the Looking Glass Symposium highlights how the field has evolved and how it impacts the lives of children and their parents. Furthermore, workshops will be held for families and professionals who are interested in learning more about the benefits of ABA. There will also be discussions about the future of the field in this region. So, it is essential to understand the social significance of ABA before implementing it.
Analytical component
The seven dimensions of ABA therapy are based on scientific methods and core principles. All interventions provided through ABA services must fall within one of these principles. Each intervention must be supported by research, practical and socially significant, and monitored closely to ensure it works. Additionally, every intervention should be adapted and evaluated if it is not practical. The seven dimensions also provide a framework for developing and evaluating behavioral interventions.
In ABA, the analytical component is considered successful when the analyst manipulates the target behavior in a controlled laboratory environment. This can be relatively easy in a controlled laboratory but impossible outside. There are two ethical methodologies for manipulating target behavior: multiple baseline design and reversal design. In addition to these, the authors outline their methodology for manipulating behavior. Finally, the authors suggest a method that combines these two aspects of ABA.
The social significance of behavior is another crucial factor in ABA. For example, nonapplied researchers might study how people eat. The latter, meanwhile, may attempt to change the eating behaviors of individuals. This difference in approach is the key to ABA’s effectiveness. The research must be able to measure and observe the behavior to make the intended changes. By understanding the seven dimensions of ABA, you will be better equipped to implement effective behavioral change.
ABA is a scientifically validated treatment for people with autism. Registered behavior technicians and Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) identify the reasons behind the behavior and use data-driven analysis to determine appropriate strategies to increase independence. The methods used to treat autism are based on decades of published research. ABA treatment plans are based on the seven dimensions. A good ABA program will have a variety of strategies to encourage independence in the child.




