Do I Need To Check My Blood Sugar While Taking Metformin?
If your diabetes is stable and you take metformin alone, you probably won’t need a glucometer to check your blood sugar levels. However, assessing your HbA1c every three to six months is crucial.
How Often Should You Check Your Blood Sugar When Taking Metformin?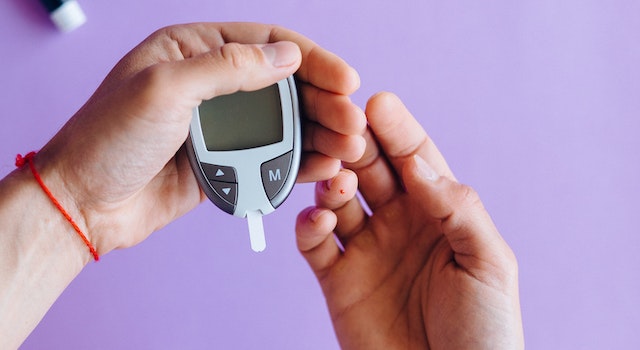
The good news is that “A patient with well-controlled type 2 diabetes who’s treated with metformin (an oral medication) may only check their glucose a few times a week or month,” says Dr. Kohlenberg. (If you suffer from type 1 diabetes and can administer multiple insulin injections daily, you’ll require greater frequency of monitoring.)
Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin
For those with well-controlled type 2 diabetes treated with metformin, blood sugar monitoring might be a bit less frequent than other treatment methods. According to Dr. Kohlenberg, an endocrinologist who is well-controlled with type 2 diabetes and taking metformin may only have to monitor their glucose levels once or twice each week or month.
The lower regularity of checking is due to the efficiency of metformin in controlling blood sugar levels. Metformin improves the sensitivity of insulin, reduces the production of glucose within the liver, and ensures more steady blood sugar levels throughout the day. This means those with consistent blood sugar control taking metformin might not require regular monitoring.
Individualized Monitoring Needs
It is important to remember that the frequency of monitoring blood sugar when taking metformin could differ based on specific aspects, such as the specific treatment plan, overall health, and the ability to adhere to lifestyle and medication changes. The guidelines in this article are intended to be an overview, and it is essential to speak with an expert in healthcare for specific guidance.
Type 1 diabetics requiring several insulin injections daily generally have different monitoring requirements compared to those with healthy type 2 diabetes. The management of Type 1 diabetes typically requires regular monitoring to regulate insulin doses and prevent episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Additionally, certain circumstances may require regular monitoring of blood sugar. For instance, during stress, illness, or changes in medication or lifestyle, it is possible to check the blood sugar levels more often to ensure optimal control and make the necessary adjustments.
How Long Does It Take For Metformin To Lower Blood Sugar?
How long will it take for it to be effective? Metformin doesn’t immediately lower blood sugar levels. The effects are usually evident within 48 hours after being prescribed the drug, but the most noticeable effects last 4-5 days before they manifest. However, the time frame depends on the individual’s dosage.
Metformin’s Onset of Action
Metformin doesn’t take effect immediately to reduce blood sugar levels. It will take a while for the drug to affect glucose metabolism and achieve optimal control of glycemic levels. The onset time for action is different for each person and will depend on many factors, such as the dosage, metabolism of the individual, and general health.
In general, the effects of metformin are typically visible within the first 48 hours after taking the medication. However, it can take up to 4-5 days for the most dramatic effects to show. In this period, metformin gradually begins to decrease glucose production in the liver and increase insulin sensitivity in body tissues.
Individual Variations in Response
The time needed for metformin to reduce blood sugar levels may differ from person to person. Numerous factors contribute to individual variations, including the dose of prescribed metformin, the degree of insulin resistance, and overall health.
For some people, the effect of metformin might be more apparent than for others. This is due to differences in the rate at which their bodies metabolize the medication or the degree of insulin resistance they experience. It is important to remember that metformin isn’t an instant fix. It’s a treatment used over time to maintain blood sugar levels.
It’s important to note that metformin is typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment program incorporating lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular physical activity. These lifestyle changes could help improve blood sugar control and enhance metformin’s effects.
Is Blood Sugar Higher After Starting Metformin?
If taken as directed, metformin is extremely efficient at decreasing blood sugar. However, you might have occasional spikes in blood sugar levels due to stress, eating a large meal, or other reasons. In most cases, you don’t have to be concerned about these sporadic spikes.
Factors Contributing to Temporary Blood Sugar Increases
Various factors can trigger temporary rises in blood sugar levels, even if metformin is taken as directed. These include stress, eating a large meal with many carbohydrates and certain medications, illnesses or hormonal changes, and insufficient adherence to lifestyle changes.
Physical and emotional stress can trigger the release of hormones that increase blood sugar levels. In the same way, eating a huge carbohydrate meal may cause a temporary rise in blood sugar. In these instances, the effect of metformin might not be enough to offset the immediate effects of these causes on blood sugar levels.
In addition, other medications, like corticosteroids or certain antipsychotics, may affect the control of blood sugar levels and cause temporary rises. The effects of illness, especially infections, can also result in increased blood sugar levels due to the release of stress hormones by the body. Hormonal changes, including those during menstrual cycles, may also affect blood sugar levels.
Understanding Occasional Increases and Managing Expectations
It is important to remember that minor rises in blood sugar levels while taking metformin are not unusual and generally don’t cause concern. Metformin remains effective for the general control of glycemic levels, and the temporary changes do not affect its long-term benefits.
Diabetes management is a fluid process that requires keen attention to various factors. It is essential to maintain an equilibrist approach by following the prescription medication and a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, reducing stress levels, and observing blood sugar levels regularly. By incorporating these changes into your lifestyle and maintaining constant communication with health professionals, people can effectively enhance their control over blood sugar and handle the occasional spikes.
You should speak with your doctor if you experience constant or prolonged rises in your blood sugar levels after taking metformin. They can assess your specific situation, adjust the treatment regimen if needed, and offer advice to assist you in achieving greater control of your glycemic levels.
Can I Miss Taking Metformin One Day?
If you do not take a metformin dose, do not take the following dose at the normal time. Don’t take two doses to make up for an unintentional dose. If you frequently forget doses, setting an alarm that reminds you could be helpful.
Skipping the Missed Dose and Maintaining the Regular Schedule
If you miss the metformin dose, you should not be anxious or overcompensated by taking a second dose to make up for the missed dose. Instead, follow these guidelines, avoid the missed dose, and proceed with your regular dose schedule. Two doses at once can increase the chance of adverse reactions or side effects.
Metformin can cause a cumulative effect throughout the body. Regular usage over time is essential to achieving the highest blood sugar levels. If you follow your routine dosing schedule, you can maintain an even amount of the medication within your body and avoid any potential interruptions in your treatment program. If you’re unsure what to do after missing the dose, speaking with your physician for individualized advice is always recommended.
Strategies to Improve Medication Adherence
The absence of a dose of metformin can be an opportunity to increase medication adherence. Here are some practical tips to remind you that you must take your medication on time:
- Set an alarm: Use reminders or alarms on your mobile device or other gadgets to remind you that you take your medication at scheduled times. This can be particularly helpful for those with a busy schedule or who easily forget routine tasks.
- Medication Organizer: Think about using a pill organizer to organize your medication during the week. This could provide visual cues and help you track whether you took your metformin dose for the day.
- Incorporate it into your Daily Routine: Incorporate the medication into a certain routine or habit. For instance, you can take it before or after eating or make it a part of a regular habit, such as brushing your teeth.
- Inform: Supportive People and share the medication regimen with a trusted family member or friend who can assist you.
Be aware that consistency in taking metformin is crucial to maintaining a steady blood sugar level and maximizing the effects of the drug. If you often cannot take your medication, discuss the problem with your healthcare professional. They can offer additional strategies and help improve your medication adherence and diabetes management.
FAQ’s
Why is it important to check my blood sugar while taking Metformin?
Checking your blood sugar regularly while on Metformin helps monitor how well the medication is controlling your diabetes. It allows you and your healthcare provider to make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan if needed.
How often should I check my blood sugar if I’m on Metformin?
The frequency of blood sugar checks can vary depending on your diabetes management plan. Typically, people on Metformin may need to check their blood sugar levels at least once a day or as advised by their healthcare provider.
Can Metformin cause low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia)?
Metformin is not known to cause hypoglycemia when used alone, but it may lead to low blood sugar levels when combined with other diabetes medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. Regular blood sugar monitoring can help detect and prevent episodes of low blood sugar.
What should I do if my blood sugar levels are consistently high while on Metformin?
If your blood sugar levels remain consistently high despite taking Metformin, it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage, recommend additional medications, or suggest lifestyle changes to better manage your diabetes.
Are there any specific times of the day when I should check my blood sugar while on Metformin?
The timing of blood sugar checks can vary based on individual circumstances and treatment plans. Some people may be advised to check their fasting blood sugar in the morning, while others may need to monitor before meals or after meals. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Can I stop checking my blood sugar once my diabetes is well-controlled with Metformin?
It is not recommended to stop monitoring your blood sugar solely because your diabetes appears to be under control with Metformin. Regular monitoring helps identify trends and ensures that your diabetes management remains effective. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice regarding blood sugar testing.
Do I Need To Check My Blood Sugar While Taking Metformin?
If your diabetes is stable and you take metformin alone, you probably won’t need a glucometer to check your blood sugar levels. However, assessing your HbA1c every three to six months is crucial.
How Often Should You Check Your Blood Sugar When Taking Metformin?
The good news is that “A patient with well-controlled type 2 diabetes who’s treated with metformin (an oral medication) may only check their glucose a few times a week or month,” says Dr. Kohlenberg. (If you suffer from type 1 diabetes and can administer multiple insulin injections daily, you’ll require greater frequency of monitoring.)
Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin
For those with well-controlled type 2 diabetes treated with metformin, blood sugar monitoring might be a bit less frequent than other treatment methods. According to Dr. Kohlenberg, an endocrinologist who is well-controlled with type 2 diabetes and taking metformin may only have to monitor their glucose levels once or twice each week or month.
The lower regularity of checking is due to the efficiency of metformin in controlling blood sugar levels. Metformin improves the sensitivity of insulin, reduces the production of glucose within the liver, and ensures more steady blood sugar levels throughout the day. This means those with consistent blood sugar control taking metformin might not require regular monitoring.
Individualized Monitoring Needs
It is important to remember that the frequency of monitoring blood sugar when taking metformin could differ based on specific aspects, such as the specific treatment plan, overall health, and the ability to adhere to lifestyle and medication changes. The guidelines in this article are intended to be an overview, and it is essential to speak with an expert in healthcare for specific guidance.
Type 1 diabetics requiring several insulin injections daily generally have different monitoring requirements compared to those with healthy type 2 diabetes. The management of Type 1 diabetes typically requires regular monitoring to regulate insulin doses and prevent episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Additionally, certain circumstances may require regular monitoring of blood sugar. For instance, during stress, illness, or changes in medication or lifestyle, it is possible to check the blood sugar levels more often to ensure optimal control and make the necessary adjustments.
How Long Does It Take For Metformin To Lower Blood Sugar?
How long will it take for it to be effective? Metformin doesn’t immediately lower blood sugar levels. The effects are usually evident within 48 hours after being prescribed the drug, but the most noticeable effects last 4-5 days before they manifest. However, the time frame depends on the individual’s dosage.
Metformin’s Onset of Action
Metformin doesn’t take effect immediately to reduce blood sugar levels. It will take a while for the drug to affect glucose metabolism and achieve optimal control of glycemic levels. The onset time for action is different for each person and will depend on many factors, such as the dosage, metabolism of the individual, and general health.
In general, the effects of metformin are typically visible within the first 48 hours after taking the medication. However, it can take up to 4-5 days for the most dramatic effects to show. In this period, metformin gradually begins to decrease glucose production in the liver and increase insulin sensitivity in body tissues.
Individual Variations in Response
The time needed for metformin to reduce blood sugar levels may differ from person to person. Numerous factors contribute to individual variations, including the dose of prescribed metformin, the degree of insulin resistance, and overall health.
For some people, the effect of metformin might be more apparent than for others. This is due to differences in the rate at which their bodies metabolize the medication or the degree of insulin resistance they experience. It is important to remember that metformin isn’t an instant fix. It’s a treatment used over time to maintain blood sugar levels.
It’s important to note that metformin is typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment program incorporating lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular physical activity. These lifestyle changes could help improve blood sugar control and enhance metformin’s effects.
Is Blood Sugar Higher After Starting Metformin?
If taken as directed, metformin is extremely efficient at decreasing blood sugar. However, you might have occasional spikes in blood sugar levels due to stress, eating a large meal, or other reasons. In most cases, you don’t have to be concerned about these sporadic spikes.
Factors Contributing to Temporary Blood Sugar Increases
Various factors can trigger temporary rises in blood sugar levels, even if metformin is taken as directed. These include stress, eating a large meal with many carbohydrates and certain medications, illnesses or hormonal changes, and insufficient adherence to lifestyle changes.
Physical and emotional stress can trigger the release of hormones that increase blood sugar levels. In the same way, eating a huge carbohydrate meal may cause a temporary rise in blood sugar. In these instances, the effect of metformin might not be enough to offset the immediate effects of these causes on blood sugar levels.
In addition, other medications, like corticosteroids or certain antipsychotics, may affect the control of blood sugar levels and cause temporary rises. The effects of illness, especially infections, can also result in increased blood sugar levels due to the release of stress hormones by the body. Hormonal changes, including those during menstrual cycles, may also affect blood sugar levels.
Understanding Occasional Increases and Managing Expectations
It is important to remember that minor rises in blood sugar levels while taking metformin are not unusual and generally don’t cause concern. Metformin remains effective for the general control of glycemic levels, and the temporary changes do not affect its long-term benefits.
Diabetes management is a fluid process that requires keen attention to various factors. It is essential to maintain an equilibrist approach by following the prescription medication and a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, reducing stress levels, and observing blood sugar levels regularly. By incorporating these changes into your lifestyle and maintaining constant communication with health professionals, people can effectively enhance their control over blood sugar and handle the occasional spikes.
You should speak with your doctor if you experience constant or prolonged rises in your blood sugar levels after taking metformin. They can assess your specific situation, adjust the treatment regimen if needed, and offer advice to assist you in achieving greater control of your glycemic levels.
Can I Miss Taking Metformin One Day?
If you do not take a metformin dose, do not take the following dose at the normal time. Don’t take two doses to make up for an unintentional dose. If you frequently forget doses, setting an alarm that reminds you could be helpful.
Skipping the Missed Dose and Maintaining the Regular Schedule
If you miss the metformin dose, you should not be anxious or overcompensated by taking a second dose to make up for the missed dose. Instead, follow these guidelines, avoid the missed dose, and proceed with your regular dose schedule. Two doses at once can increase the chance of adverse reactions or side effects.
Metformin can cause a cumulative effect throughout the body. Regular usage over time is essential to achieving the highest blood sugar levels. If you follow your routine dosing schedule, you can maintain an even amount of the medication within your body and avoid any potential interruptions in your treatment program. If you’re unsure what to do after missing the dose, speaking with your physician for individualized advice is always recommended.
Strategies to Improve Medication Adherence
The absence of a dose of metformin can be an opportunity to increase medication adherence. Here are some practical tips to remind you that you must take your medication on time:
- Set an alarm: Use reminders or alarms on your mobile device or other gadgets to remind you that you take your medication at scheduled times. This can be particularly helpful for those with a busy schedule or who easily forget routine tasks.
- Medication Organizer: Think about using a pill organizer to organize your medication during the week. This could provide visual cues and help you track whether you took your metformin dose for the day.
- Incorporate it into your Daily Routine: Incorporate the medication into a certain routine or habit. For instance, you can take it before or after eating or make it a part of a regular habit, such as brushing your teeth.
- Inform: Supportive People and share the medication regimen with a trusted family member or friend who can assist you.
Be aware that consistency in taking metformin is crucial to maintaining a steady blood sugar level and maximizing the effects of the drug. If you often cannot take your medication, discuss the problem with your healthcare professional. They can offer additional strategies and help improve your medication adherence and diabetes management.
FAQ’s
Why is it important to check my blood sugar while taking Metformin?
Checking your blood sugar regularly while on Metformin helps monitor how well the medication is controlling your diabetes. It allows you and your healthcare provider to make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan if needed.
How often should I check my blood sugar if I’m on Metformin?
The frequency of blood sugar checks can vary depending on your diabetes management plan. Typically, people on Metformin may need to check their blood sugar levels at least once a day or as advised by their healthcare provider.
Can Metformin cause low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia)?
Metformin is not known to cause hypoglycemia when used alone, but it may lead to low blood sugar levels when combined with other diabetes medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. Regular blood sugar monitoring can help detect and prevent episodes of low blood sugar.
What should I do if my blood sugar levels are consistently high while on Metformin?
If your blood sugar levels remain consistently high despite taking Metformin, it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage, recommend additional medications, or suggest lifestyle changes to better manage your diabetes.
Are there any specific times of the day when I should check my blood sugar while on Metformin?
The timing of blood sugar checks can vary based on individual circumstances and treatment plans. Some people may be advised to check their fasting blood sugar in the morning, while others may need to monitor before meals or after meals. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Can I stop checking my blood sugar once my diabetes is well-controlled with Metformin?
It is not recommended to stop monitoring your blood sugar solely because your diabetes appears to be under control with Metformin. Regular monitoring helps identify trends and ensures that your diabetes management remains effective. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice regarding blood sugar testing.